
Enrichment Therapy and Learning Center is one of the wonderful resources for Dyslexia in the Iowa City/Coralville Corridor area. They graciously agreed to write a blog post for our followers. We are grateful for the care they provide, and are glad to have Enrichment Therapy in our area. This blog-post was written by Kristin Ebeling of Enrichment Therapy.
Dyslexia is a very important and a very real concern for many students
Parents often confuse the terms dyslexia and reading disorder. These terms are frequently used interchangeably, despite the difference in meaning. To help ease the confusion, I have outlined the differences between the terms dyslexia and reading disorder so you feel better educated and are able to use them accurately in the future!
What is Dyslexia?
Dyslexia is a type of reading disorder. According to the Decoding Dyslexia Healthcare Screening, “Dyslexia is a specific learning disability that is neurological in origin. It is characterized by difficulties with accurate and/or fluent word recognition and by poor spelling and decoding abilities.” Dyslexia is primarily a disorder of phonological processing and reading fluency. Students with dyslexia often struggle to identify the sounds for a particular letter or segment a group of letters. This in turn affects the ability to read words and paragraphs fluently, to spell words, and to use words in writing. Struggles frequently increase as reading demands increase.
The Grey Oral Reading Test-5 a scaled score of 8-12 is considered the average range. Student A is an example of a profile that may suggest dyslexia.
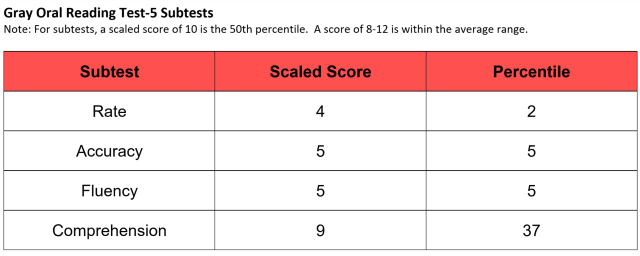
Student A:
This student’s reading fluency, both accuracy and rate, fell moderately below the average range. However, their reading comprehension was age-appropriate. This student may be diagnosed with dyslexia if his/her delays in reading fluency co-occur with other risk factors such as:
- Difficulty with rhyming
- Difficulty pronouncing words that have multiple syllables
- Difficulty making connections between sounds and letters
- Difficulty recognizing words that begin with same sound
- Difficulty clapping their hands to the rhythm of a beat
- Difficulty learning to write
- Difficulty distinguishing different sounds in words
- Difficulty in learning the sounds of letters
- Inserting extra letters, deleting letters, or switching the order of letters when spelling
“Dyslexia is primarily a disorder of phonological processing and reading fluency.”
-Enrichment Therapy, North Liberty
What is a Reading Disorder?
Reading disorder is an “umbrella” or general term that refers to a larger category of disorders that interfere with a student’s ability to read. According to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, labels for reading disorders include :
- dyslexia
- reading disability
- reading disorder
- specific reading disorder
- specific reading comprehension deficit
According to the Encyclopedia of Mental Disorders, a reading disorder “involves significant impairment of reading accuracy, speed, or comprehension to the extent that the impairment interferes with academic achievement or activities of daily life.” A student with a reading disorder may have impaired phonological processing skills, reading comprehension, and/or reading fluency.
- Phonological processing is a student’s ability to detect and create rhyming words, break words into syllables, identify individual sounds at the beginning or end of words, and isolate/substitute/or delete individual sounds within a word. These skills are also known as the “building blocks” of reading success.
- Reading comprehension refers to the student’s ability to understand written content and reading fluency refers to the student’s accuracy and rate while reading. Check out this blog from September of 2017 for more information about the difference between reading fluency and comprehension here!
- Difficulties in any of these three skills may be classified as a reading disorder. A test we frequently give to evaluate a student’s reading abilities is the Grey Oral Reading Test-5. On this test, a scaled score of 8-12 is considered the average range.
Students B and C are examples of profiles that may suggest a reading disorder.
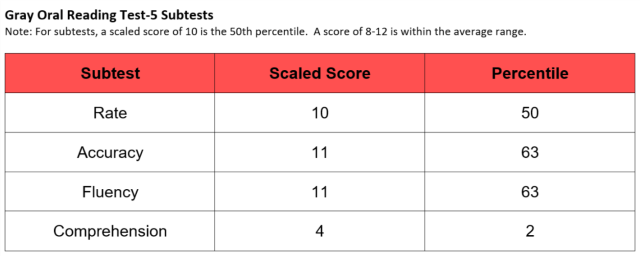
Student B:
This student’s reading fluency was age-appropriate. However, their reading comprehension fell moderately below the average range. This student may be diagnosed with a Reading Disorder.
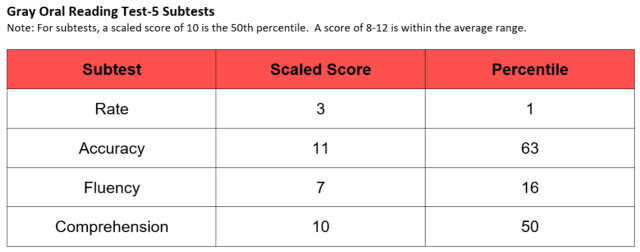
Student C:
This student’s reading rate fell moderately below the average range. However, their reading comprehension and accuracy was age-appropriate. This student may be diagnosed with a Reading Disorder.
“A student with a reading disorder may have impaired phonological processing skills, reading comprehension, and/or reading fluency.”
-Enrichment Therapy, North Liberty
In summary, Dyslexia is a specialized term for a specific type of reading disability characterized by difficulties with phonological processing and reading fluency. A reading disorder is a generic term for a specific learning disability in areas of phonological processing, reading comprehension, and/or reading fluency.
Click here to learn more about the Enrichment Therapy & Learning Center. They provide individual speech language therapy and tutoring as well as offer a unique group, the Language Enrichment Academic Program (LEAP). At Enrichment Therapy and Learning Center, their passion is to help kids achieve effective communication skills and gain academic success.
At Hope Springs, we provide neuropsychological evaluations to find out WHY children are having reading concerns or Dyslexia. Oftentimes, in addition to speech and language concerns, children may struggled with attention concerns, concerns with executive functioning, memory concerns, learning difficulties, and lots of worries or stress. In these circumstances, we will work together with you to help take the next steps. We are glad to have colleagues, like those at Enrichment Therapies to help serve children and adolescents in our community. It truly does take a village.
![]()
